This is a newly opened window. When finished viewing this window, please
close it.
ALPHA ADRENERGIC AGONISTS (Central Acting)
GOOGLE SPONSORED ADS
SIMPLE MECHANISMS OF ACTIONS - HYPERTENSION MEDICATIONS
NOTE: In addition to the information presented here, other mechanisms are
also involved in the antihypertensive effects of most of these hypertension
medications.
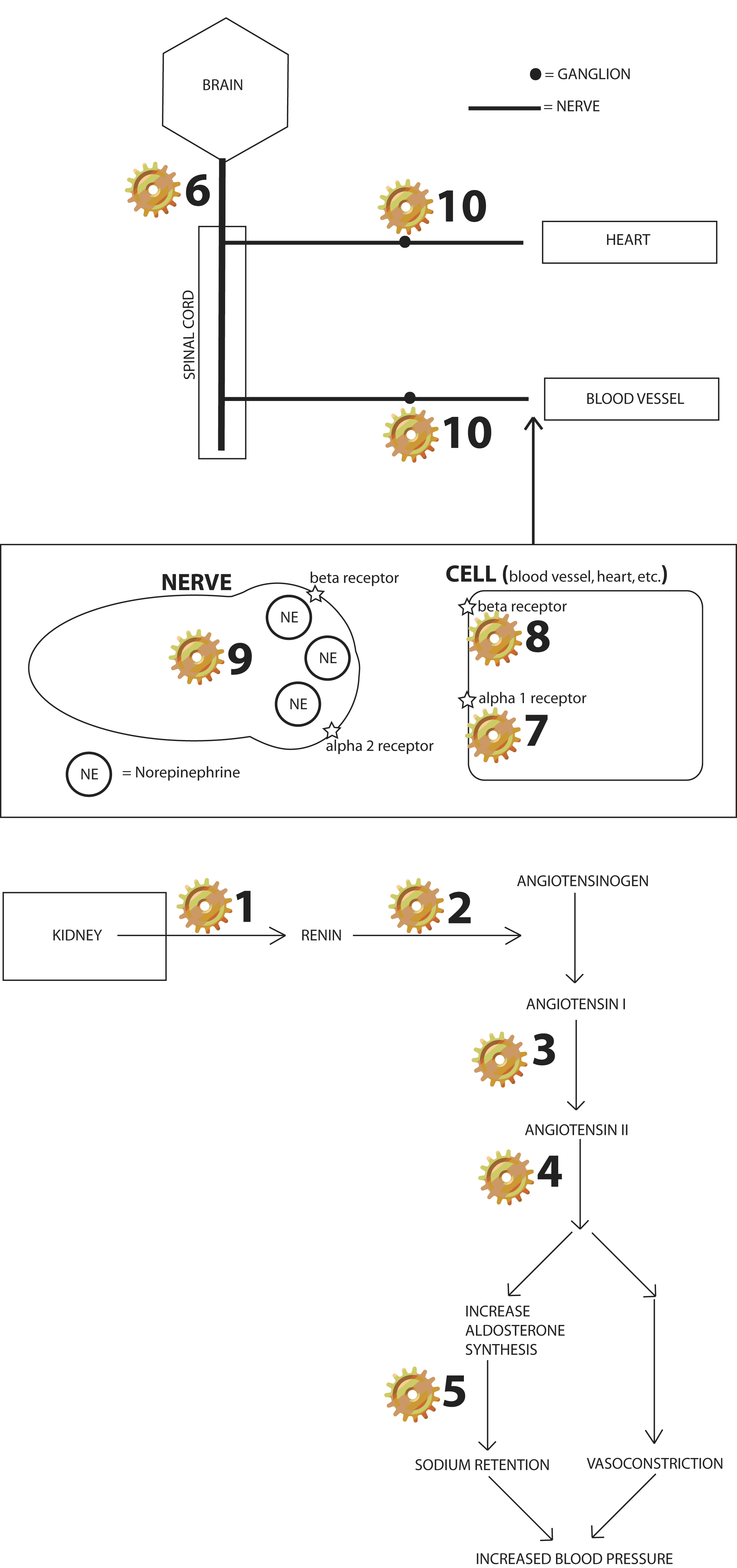
The graphic below on the left is
(a) - representation of the sympathetic nervous system and its actions on body
tissues such as heart, kidney, and blood vessels.
(b) - The chemical actions involved in blood pressure regulations.
 7,
8, 9 is an enlarged representation of the synaptic space between the nerve and
the cell (blood vessel, heart, etc). Catecholamines (dopamine,
norepinephrine in the postganglionic nerve endings, and epinephrine from the
adrenal gland) all induce vasoconstriction by activating the post synaptic alpha
1 receptor.
7,
8, 9 is an enlarged representation of the synaptic space between the nerve and
the cell (blood vessel, heart, etc). Catecholamines (dopamine,
norepinephrine in the postganglionic nerve endings, and epinephrine from the
adrenal gland) all induce vasoconstriction by activating the post synaptic alpha
1 receptor.
Norepinephrine is released from the nerve and acts on the
post synaptic alpha receptor. This induces vasoconstriction. The pre
synaptic alpha 2 receptor provides feedback to inhibit additional release of
norepinephrine.
Agonists - This class of medications attach and activate
the receptor.
Antagonists - This class of medications attach to the
receptor, but does not activate the receptor. Therefore, this class of
medications blocks the receptor and antagonize the natural receptor agonist.
Alpha Receptor Action: Blood Vessel -
vasoconstriction (narrows vessel).
Beta Receptor Action: Kidney - increase renin secretion; Heart
- increase heart rate, contractility, conduction, excitation; Lung -
increase bronchodilation (opens lungs); Blood Vessel - vasodilation
(opens vessel).
| |
 6
Alpha Adrenergic Agonists (central acting) 6
Alpha Adrenergic Agonists (central acting)
Examples: clonidine, methyldopa, guanabenz
These meds acts by stimulating the central alpha receptors which
depresses or inhibits sympathetic nerve activity (decreasing
catecholamine [norepinephrine] release). This central action also causes
side effects such as dry mouth, sedation, decreased alertness, and
rebound hypertension when stopped abruptly. |
| |
 10
Ganglion Blockers 10
Ganglion Blockers
Examples: inversine (mecamylamine)
Acetylcholine is released from the preganglionic nerve which binds to
and stimulates the nicotinic receptors on the cell bodies of the
postganglionic nerve. This causes increased sympathetic tone and
vascular contraction which increases cardiac output and blood pressure.
These meds block the ganglion of the nerve which blocks the
acetylcholine binding and stimulation of the receptors. |
| |
 9
Adrenergic Neuron Antagonists (periherally acting) 9
Adrenergic Neuron Antagonists (periherally acting)
Examples: reserpine, rauwolfia, guanadrel.
Interferes with the release of norepinephrine at the sympathetic nerve
endings (peripheral).
This results in a decrease in peripheral resistance which lowers blood
pressure. |
| |
 7
Alpha Adrenergic Blockers 7
Alpha Adrenergic Blockers
Examples: minipress, hytrin, cardura
The effect is due to the blocking of the post synaptic alpha receptor.
This prevents norepinephrine from acting on the receptor.
The pre synaptic alpha 2 receptor is not affected, allowing the feedback
inhibition of additional norepinephrine release. |
| |
 8
Beta Adrenergic Blockers 8
Beta Adrenergic Blockers
Examples: propranolol, metoprolol
Beta receptors stimulations causes increase
renin secretion, increase heart rate, contractility, conduction,
excitation, increase bronchodilation, and vasodilation (opens vessel).
These meds competes with catecholamines (norepinephrine)
for binding to the beta adrenergic receptors in
vascular smooth muscles and in the heart. This blocking of the
beta receptors results in decreasing beta stimulation and the effects of
the catecholamines. Blood pressure is decreased. |
| |
 1
Beta Adrenergic Blockers 1
Beta Adrenergic Blockers
Examples: propranolol, metoprolol
Beta receptors stimulations causes increase
renin secretion.
This blocking of the beta receptors results in decreasing beta
stimulation and renin secretion. Blood pressure is decreased. |

 8 8
 7 7
 1
Alpha & Beta Adrenergic Blockers 1
Alpha & Beta Adrenergic Blockers
Examples: coreg, normodyne, trandate
Also see information on alpha blockers and beta blockers.
The ratio of alpha blocking and beta blocking may be variable depending
on the specific medication.
Plasma renin activity decreases and catecholamine (norepinephrine)
increases.
Blood pressure decreases mainly by decreasing vascular resistance. |
| |
 2
Inhibition of Renin 2
Inhibition of Renin
Example: Tekturna
These medications inhibit the production of renin , angiotensin I, and angiotensin
II. |
| |
 3
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors 3
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
Accupril, monopril, vasotec, zestril
These meds block the production of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. This
decreases aldosterone and its sodium retention and decreases angiotensin
II and its vasoconstriction. Renin release increases. |
| |
 4
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers 4
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers
Examples: Avapro, Cozaar, Diovan
These meds bind to the AT1-receptors and thereby interfere with the
binding of angiotensin II to the angiotensin II receptor. By
blocking angiotensin II (which is a vasoconstrictor and which increase
synthesis and release of aldosterone), these meds cause a decrease in
vascular resistance and thereby decreases blood pressure. Renin release
increases. |
| |
 5
Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist (mineralcorticoid* receptor blocker) 5
Aldosterone Receptor Antagonist (mineralcorticoid* receptor blocker)
Examples: Inspra
The effect is due to the binding to the mineralcorticoid receptor and
blocking the binding of aldosterone to the receptor. If aldosterone
binds to these receptors found in tissues (including blood vessels,
heart, kidney, and brain), blood pressure is increased by the increase
sodium reabsorption (retention).
By blocking the negative feedback regulation of aldosterone on renin,
the increase plasma renin increases serum aldosterone. The increased
renin and aldosterone levels do not overcome the effects of the
aldosterone receptor antagonist. |
CORTICOSTEROIDS
a. Glucocorticoids (cortisol, hydrocortisone)
b. *Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) - causes kidney to reabsorb sodium
and
water, and secretion of potassium)
c. Androgens (testosterone)
d. Estrogens
e. Progestagens (progesterone) |
| |
| ---OTHERS NOT SHOWN ON GRAPHICS--- |
 A
Calcium Channel Blockers A
Calcium Channel Blockers
Examples: norvasc, procardia.
These meds inhibit calcium influx in heart and blood vessel smooth
muscle cells. The decrease in calcium in the cells decreases the muscle
contraction resulting in decreased myocardial contractility and dilation
of the blood vessels (vasodilation). This causes decreased
peripheral resistance and a decrease in blood pressure. |
| |
 B
Thiazide & Related Diuretics B
Thiazide & Related Diuretics
Examples: lasix, hydrochlorothiazide.
These meds increase water loss from the body by inhibiting
sodium/chloride reabsorption in the kidneys. Thiazides also increase
potassium excretion by the kidneys. By reducing water (extracellular
fluid volume), the blood pressure is lowered. Thiazides also cause
vasodilation which reduces peripheral vascular resistance. |
| |
 C
Vasodilators (direct relaxation of vascular smooth muscles) C
Vasodilators (direct relaxation of vascular smooth muscles)
Examples: hydralazine, minoxidil.
These meds cause direct relaxation of vascular smooth muscles and
produces decreased vascular resistance.
The mechanism of action of hydralazine is not known.
Minoxidil increases potassium conductance in vascular smooth muscle and
the resultant hyperpolarization reduces calcium entry.
The direct vasodilation causes the body to respond by increasing heart
rate and cardiac output. The renin-angiotensin system causes aldosterone
release which results in sodium and fluid retention.
Beta blockers can help the increased heart rate and cardiac output.
Diuretics can help the fluid retention. |
| |
![]() 7,
8, 9 is an enlarged representation of the synaptic space between the nerve and
the cell (blood vessel, heart, etc). Catecholamines (dopamine,
norepinephrine in the postganglionic nerve endings, and epinephrine from the
adrenal gland) all induce vasoconstriction by activating the post synaptic alpha
1 receptor.
7,
8, 9 is an enlarged representation of the synaptic space between the nerve and
the cell (blood vessel, heart, etc). Catecholamines (dopamine,
norepinephrine in the postganglionic nerve endings, and epinephrine from the
adrenal gland) all induce vasoconstriction by activating the post synaptic alpha
1 receptor.
